Photoaging - also known as sun damage, photodamage, and premature aging - is a condition primarily caused by regular exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun. While age plays a role, dermatologists assert that about 70% of skin aging is attributed to the negative effects of UV rays. This article explores the phenomenon of photoaging, its signs, vulnerable groups, and effective prevention strategies.
What is Photoaging (Sun Damage)?
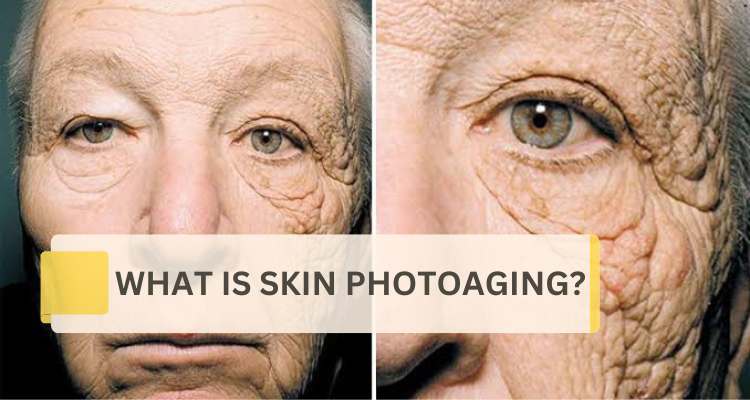
Photoaging, also known as sun damage, refers to the premature aging of the skin caused by prolonged and repeated exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources, such as tanning beds. Unlike chronological aging, which occurs naturally over time, photoaging accelerates the aging process and results in specific signs and changes in the skin's appearance.
The primary contributor to photoaging is the harmful effect of UV rays on the skin. UV radiation penetrates the skin and damages the underlying collagen and elastin fibers, leading to a loss of skin elasticity and the formation of wrinkles. Additionally, UV exposure triggers the production of free radicals, which can further damage skin cells and contribute to the aging process
What are the Signs of Photoaging (Sun Damage)?
Photoaging, or sun damage, is characterized by a variety of visible signs on the skin, and these signs typically manifest in areas that have been exposed to the sun over an extended period. The common signs of photoaging include:
- Wrinkles and Fine Lines: Excessive sun exposure contributes to the breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers, leading to the formation of wrinkles, especially around the eyes, mouth, and forehead.
- Hyperpigmentation: Uneven skin tone, dark spots, and sunspots are common signs of photoaging. These areas of hyperpigmentation result from an overproduction of melanin in response to sun exposure.
- Loss of Skin Elasticity: The skin may lose its firmness and resilience, leading to sagging and a less supple appearance.
- Texture Changes: Photoaged skin may become rough, dry, and exhibit a leathery texture due to damage to the skin's outer layer.
- Broken Blood Vessels (Telangiectasia): Visible small blood vessels near the surface of the skin, often seen on the face, as a result of sun-induced damage.
- Sunburn and Redness: Chronic sun exposure can cause persistent redness and inflammation, contributing to an overall aged appearance.
- Actinic Keratosis: Rough, scaly patches on the skin that may be precancerous and are associated with prolonged sun exposure.
- Dilated Pores: Sun damage can enlarge and dilate pores, affecting the skin's texture and appearance.
- Dryness and Thinning Skin: Dehydrated skin and a reduction in the thickness of the skin are common consequences of photoaging.
- Liver Spots (Lentigines): Dark, flat spots on the skin, commonly found on the face, hands, and other sun-exposed areas.
It's important to note that the severity of these signs can vary based on factors such as skin type, genetics, and the level of sun protection adopted throughout life. While it's challenging to reverse photoaging completely, preventive measures and skincare interventions can help minimize further damage and improve the overall appearance of sun-damaged skin.
Photoaging is cumulative, meaning that the effects of sun exposure over time contribute to the severity of these signs. Prevention through sun protection measures, such as sunscreen use, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding excessive sun exposure, is crucial in minimizing the impact of photoaging and maintaining healthy skin. Additionally, certain skincare treatments and interventions can help mitigate the visible signs of photoaged skin.
What's the difference between photoaging and chronological skin aging?
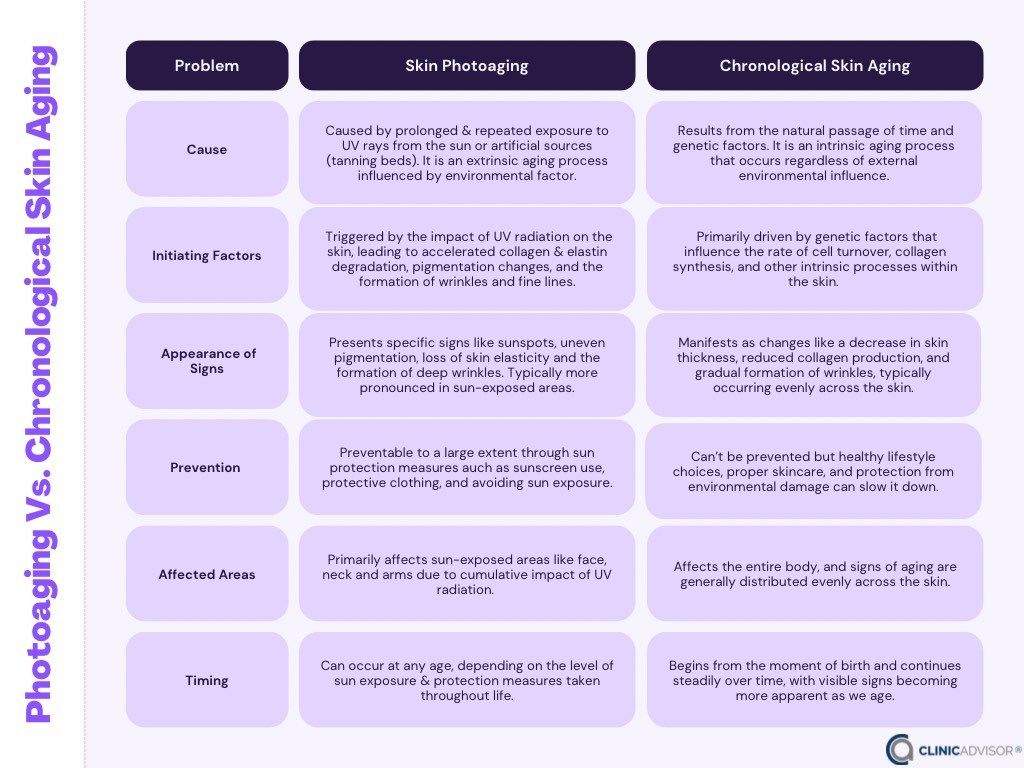
Photoaging and chronological skin aging represent distinct processes contributing to changes in the skin over time. Photoaging is primarily caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or artificial sources, constituting an extrinsic aging process influenced by environmental factors. It leads to specific signs such as sunspots, uneven pigmentation, and the formation of deep wrinkles, primarily affecting sun-exposed areas. Prevention strategies involve sun protection measures, emphasizing the use of sunscreen and protective clothing. In contrast, chronological aging results from the natural passage of time and genetic factors, constituting an intrinsic aging process independent of external influences. Signs of chronological aging, such as decreased skin thickness and collagen production, occur evenly across the skin and progress steadily throughout life. While chronological aging is inevitable, proactive measures can significantly mitigate the impact of photoaging, emphasizing the importance of tailored skincare strategies for each aging process.
How to Protect the Skin from Photoaging (Sun Damage)?
Protecting the skin from photoaging involves adopting proactive measures to minimize exposure to harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Here are key strategies to help safeguard the skin from the effects of photoaging:
- Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high Sun Protection Factor (SPF) daily, even on cloudy days. Apply it to all exposed skin, including the face, neck, and hands.
Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating. - Protective Clothing: Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses with UV protection.
Consider clothing with a built-in ultraviolet protection factor (UPF) for enhanced sun protection. - Avoid Peak Sun Hours: Limit sun exposure during peak hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV rays are most intense. You can check the UV index in your area to help you assess the intensity of the rays. Schedule outdoor activities earlier or later in the day to reduce exposure during peak sun hours.
- Seek Shade: Take breaks in shaded areas to minimize direct sun exposure. Use umbrellas or seek natural shade when spending extended periods outdoors.
- Limit Tanning Bed Use: Avoid tanning beds, as they emit harmful UVA and UVB rays, contributing to premature aging of the skin.
- Sun-Protective Skincare: Use skincare products that contain antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, to help combat free radicals generated by sun exposure. Consider moisturizers with built-in SPF for added daily protection.
- Regular Skin Check-ups: Schedule regular dermatological check-ups to monitor the health of your skin and address any concerns promptly.
- Hydration: Keep the skin well-hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water, promoting overall skin health.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Adopt a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, as these factors contribute to overall skin well-being.
- Collagen-Boosting Supplements: Consider collagen-boosting supplements, such as vitamin C and collagen peptides, to support the skin's structure and resilience.
By consistently incorporating these protective measures into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of photoaging and maintain healthier, more youthful-looking skin over time. Preventive actions are crucial in minimizing the cumulative effects of sun exposure and promoting long-term skin health.
How Can You Prevent Photoaging?
While it's challenging to entirely prevent photoaging, several proactive measures can significantly minimize its impact and delay the onset of visible signs. Here are key strategies to help prevent photoaging:
Sunscreen: Regularly apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
Protective Clothing: Wear hats, sunglasses, and clothing that provide additional coverage, especially during peak sun hours between 11 a.m. and 4 p.m.
Avoidance of Tanning Beds: Refrain from using tanning beds, as they emit harmful UVA rays that accelerate collagen damage and contribute to premature aging.
Seek Shade: Stay in the shade when possible, especially during peak sunlight hours, to reduce direct exposure to UV rays.
Antioxidant-Rich Diet: Consume a diet rich in antioxidants, particularly vitamins C and E, which can help combat free radicals generated by UV radiation. Foods like berries, citrus fruits, nuts, and leafy greens are good sources.
Hydration: Keep the skin well-hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water. Hydrated skin is more resilient and better equipped to cope with environmental stressors.
Topical Antioxidants: Use skincare products containing antioxidants like vitamins C and E. These can provide an additional layer of protection against free radicals and oxidative stress.
Regular Skin Check-ups: Schedule regular dermatological check-ups to monitor your skin's health and address any concerns early on.
Avoid Smoking: Refrain from smoking, as it can negatively impact the condition of the skin and exacerbate the effects of photoaging.
Lifestyle Choices: Adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management. These factors contribute to overall skin health.
Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can dehydrate the skin and contribute to premature aging. Limiting alcohol intake supports skin health.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can effectively reduce the risk of photoaging and promote long-term skin health. Consistent sun protection and a holistic approach to skincare contribute to maintaining youthful and resilient skin
Are there health conditions that increase your risk for sun-damaged skin?
Yes, certain health conditions can increase the risk of sun-damaged skin. Conditions that make the skin more sensitive to sunlight or compromise its ability to repair damage may elevate the risk. Some of these conditions include:
- Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP): This rare genetic disorder impairs the skin's ability to repair damage caused by UV radiation, leading to an increased risk of skin cancers and severe sunburns.
- Porphyria: A group of rare blood disorders that can cause sensitivity to sunlight, resulting in skin problems and blistering upon sun exposure.
- Albinism: Individuals with albinism have little to no melanin, making their skin highly susceptible to sun damage, including sunburns and an increased risk of skin cancers.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): Lupus can cause photosensitivity, making the skin more reactive to sunlight and potentially leading to rashes and other skin issues.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as certain antibiotics, antifungals, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can increase sensitivity to sunlight and contribute to sun damage.
- Immunosuppression: Individuals with weakened immune systems, whether due to medical conditions like HIV/AIDS or medications after organ transplantation, may be at a higher risk for skin cancers induced by UV exposure.
Individuals with these health conditions must take extra precautions when exposed to sunlight, including using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade to minimize the risk of sun damage and associated complications. Consultation with healthcare professionals is advisable to develop a personalized sun protection plan based on individual health conditions and needs.
Can sun damage be reversed?
While it's challenging to completely reverse sun damage, especially in severe cases, certain treatments and skincare practices can help improve the appearance of sun-damaged skin and minimize the associated signs. Here are some approaches to address sun damage:
Topical Treatments:
Retinoids: Prescription retinoids (such as tretinoin) can promote skin cell turnover, stimulate collagen production, and improve the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles caused by sun damage.
Topical Antioxidants: Products containing antioxidants like vitamin C can help neutralize free radicals generated by sun exposure, reducing oxidative stress on the skin.
Chemical Peels:
Chemical peels involve the application of a solution to the skin, causing the outer layer to peel off. This process can improve skin texture, reduce hyperpigmentation, and promote collagen production.
Microdermabrasion:
This procedure involves exfoliating the outer layer of the skin to encourage new skin growth. It can help reduce the appearance of sunspots and improve skin texture.
Laser Therapy:
Lasers can target specific skin concerns, such as pigmentation issues and broken blood vessels. Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) treatments are commonly used to address sun damage, targeting pigmented areas and promoting collagen production.
Dermabrasion:
Similar to microdermabrasion but more aggressive, dermabrasion involves removing the top layer of skin to improve texture and reduce the appearance of sun damage.
Injectables:
Dermal fillers can be used to plump and hydrate the skin, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles caused by sun damage.
Moisturizers and Sunscreen:
Hydrating the skin with a quality moisturizer can improve its overall appearance. Additionally, using sunscreen consistently can prevent further sun damage and protect the skin.
Hydroquinone:
This skin-lightening agent is sometimes used to reduce the appearance of dark spots caused by sun damage. However, its use should be supervised by a dermatologist due to potential side effects.
It's important to note that the effectiveness of these treatments can vary based on the severity of sun damage and individual skin characteristics. Additionally, prevention through consistent sun protection measures is crucial to maintaining skin health and preventing further damage. Consulting with a dermatologist can help determine the most appropriate and effective treatments for specific sun-related skin concerns.
Avoid the sun at critical times
Yes, avoiding sun exposure during critical times can significantly help in preventing sun damage to the skin. The sun's rays are most intense between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., and during this period, the risk of UV radiation-induced skin damage is higher. Here's how avoiding sun exposure during these critical times can be beneficial:
- Reduced UV Exposure:
Staying indoors or seeking shade during peak sun hours helps minimize direct exposure to harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. This reduces the risk of sunburn, premature aging, and the development of skin cancers.
- Lowered Risk of Sunburn:
Sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to excessive UV radiation. By avoiding the sun during its most intense hours, you decrease the likelihood of sunburn, which is not only uncomfortable but also a sign of skin damage.
- Prevention of Photoaging:
Photoaging, characterized by wrinkles, fine lines, and hyperpigmentation, is largely attributed to prolonged sun exposure. Avoiding the sun during critical times helps prevent the cumulative effects of UV radiation on the skin, promoting a healthier and more youthful complexion.
- Decreased Risk of Skin Cancer:
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation is a major risk factor for skin cancers, including melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma. Avoiding the sun during peak hours can contribute to a reduced risk of developing these types of skin cancers.
- Preservation of Skin Health:
By minimizing sun exposure during critical times, you contribute to the overall health and resilience of your skin. Healthy skin is more capable of withstanding environmental stressors and maintaining its youthful appearance.
- Enhanced Effectiveness of Sunscreen:
If you need to be outdoors during peak sun hours, using sunscreen is crucial. However, avoiding the sun during critical times complements the use of sunscreen, providing an additional layer of protection.
It's important to note that even on cloudy or overcast days, UV rays can penetrate through the clouds and cause skin damage. Therefore, adopting a sun-protective lifestyle that includes seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and using sunscreen consistently, especially during critical times, is key to maintaining skin health and preventing sun-related damage.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Who is at risk for skin damage from the sun?
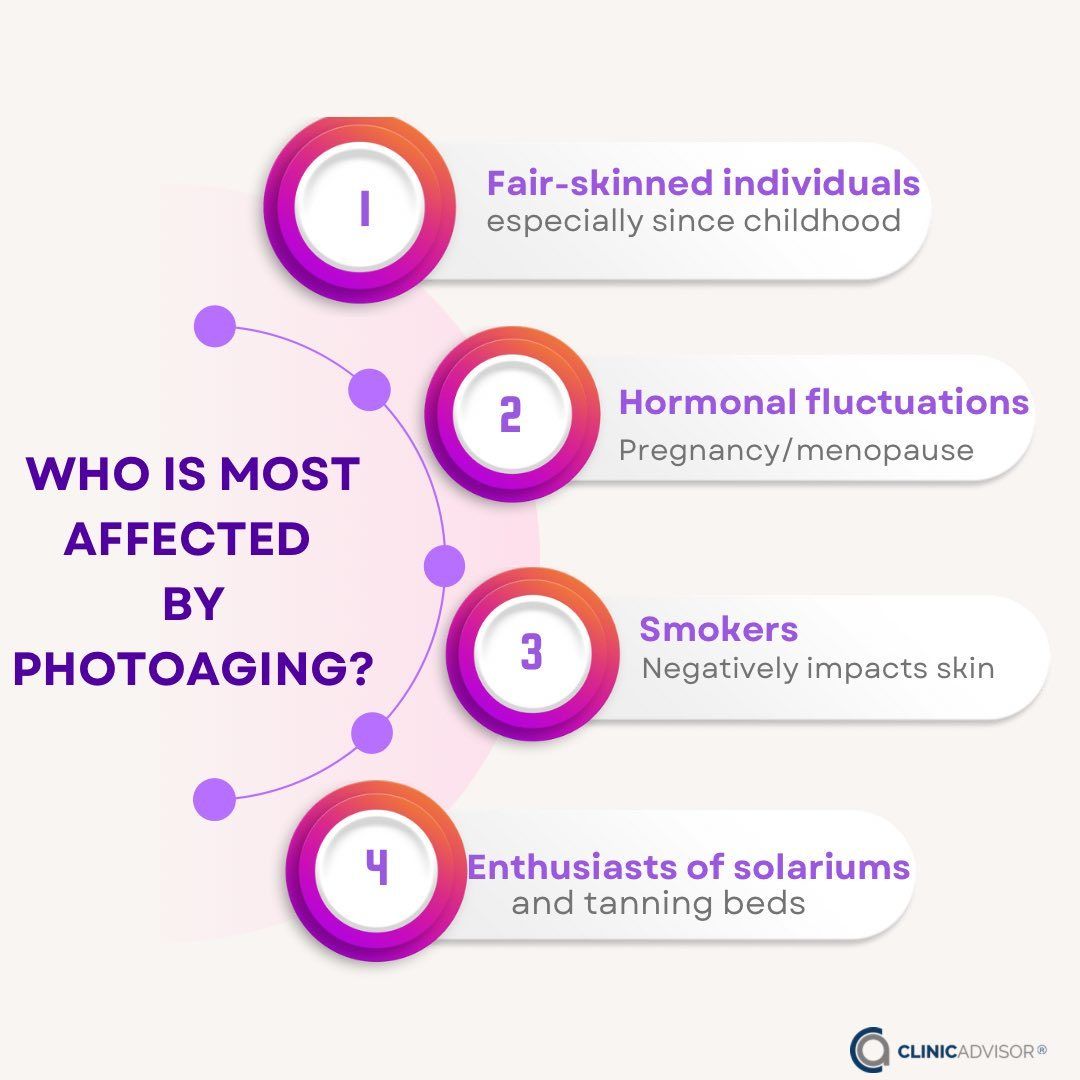
Individuals with fair skin are particularly at risk for skin damage from the sun, as their skin has less melanin, the pigment that provides some natural protection against UV radiation. Those with a history of sunburns, especially during childhood, also face an increased risk. People living in areas with intense sunlight and those with outdoor occupations or hobbies may experience prolonged sun exposure, elevating their risk. Additionally, individuals with a family history of skin cancer, those taking certain medications that increase sensitivity to sunlight, and individuals with compromised immune systems are more vulnerable to sun damage. Regardless of these risk factors, everyone is susceptible to sun damage, emphasizing the importance of sun protection measures for overall skin health.
Can sun-damaged skin be repaired?
While complete reversal of sun damage is challenging, various measures can significantly improve the appearance of sun-damaged skin. Topical treatments such as retinoids and vitamin C serums stimulate collagen production and reduce pigmentation irregularities. Professional procedures like chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion can enhance skin texture and tone by exfoliating damaged outer layers. Dermabrasion and hyaluronic acid fillers offer more aggressive options for improving skin quality. Maintaining skin health through moisturizers and sunscreen is essential in preventing further damage during the repair process. Adopting an antioxidant-rich diet, considering collagen-boosting supplements, and seeking advice from a dermatologist for personalized treatments contribute to the overall strategy of repairing sun-damaged skin. However, prevention remains paramount, emphasizing the ongoing importance of sun protection practices to preserve skin health and mitigate future damage. Consulting with skincare professionals ensures tailored approaches to individual skin concerns and helps individuals make informed decisions about their skin repair journey.
How to Revitalize skin with effective ingredients?
Photoaging, or premature aging, is a condition primarily caused by regular exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun. While age plays a role, dermatologists assert that about 70% of skin aging is attributed to the negative effects of UV rays. This article explores the phenomenon of photoaging, its signs, vulnerable groups, and effective prevention strategies.
How Can I Protect My Skin from Photoaging?
Protecting the skin from photoaging is crucial. Key measures include:
Avoid harsh sunlight: Especially between 11 a.m. and 4 p.m., when the most aggressive rays are present. Seeking shade during these hours is advisable.
Consistent use of sunscreen: Regardless of weather conditions, sunscreen is a primary defense against UV rays.
Sun protection clothing: Wearing UPF hats and UPF clothing that provide additional coverage helps reduce direct sun exposure.
Dietary supplements: Incorporating vitamin C and E supplements into the diet enhances antioxidant defenses against free radicals, contributing to the prevention of photoaging.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding the mechanisms of photoaging and taking proactive steps to protect the skin are essential for maintaining healthy and youthful-looking skin. By adopting a comprehensive approach, individuals can minimize the impact of sun-induced aging and promote long-term skin health. Regular dermatological check-ups and lifestyle changes further contribute to a holistic strategy for combating photoaging and preserving the skin's vitality.



Share Your Opinion, Please